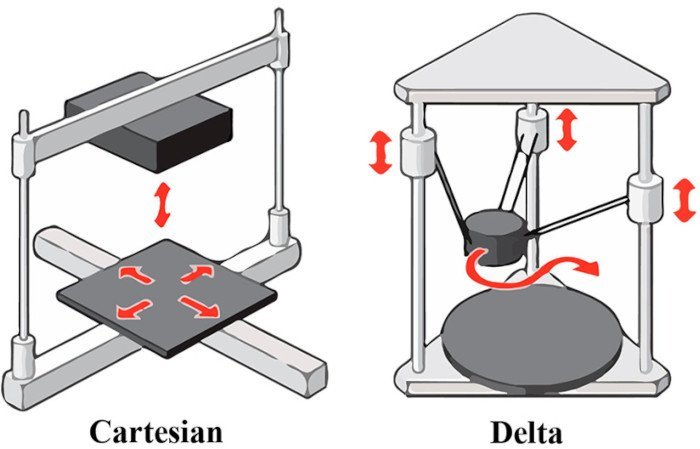
In the world of 3D printing, we often come across two common types of designs: Delta and Cartesian. Both have unique characteristics, advantages and disadvantages, but the question inevitably arises: which one is better? To summarize, while both Delta and Cartesian 3D printers are capable of creating high-quality prints, their inherent mechanical differences can make one more suitable for certain tasks than the other. **Delta printers excel in speed and precision, making them ideal for intricate, high-resolution prints. On the other hand, Cartesian printers are renowned for their large build volumes and versatility, which are advantageous for large parts and multi-material printing.** However, as with most technical comparisons, the “better” choice often boils down to individual needs and preferences.
Digging Deeper into Delta 3D Printers
Main Characteristics
Delta 3D printers, named after their triangular shape, operate using something called “delta mechanics.” This involves three parallel arms that connect the print head to the base of the printer, moving simultaneously to control the positioning of the print head. Their design provides several unique advantages, such as speedy printing, high precision, and low vibration, thanks to their lightweight print head and the reduced need for movement in the print bed.
Advantages of Delta Printers
Adopting a Delta printer into your 3D printing operation can bring a host of benefits. One of the most notable is their speed. Because the print head is so light and is moved on three axes by the stationary motors, the machine can operate at great speeds without sacrificing precision, bringing efficiency into the workflow. In addition, their unique design makes them an aesthetic choice for many, as watching a Delta 3D printer work can be captivating.
Drawbacks of Delta Printers
However, as with anything, Delta printers aren’t flawless. The main downfall of Delta’s design is their printing volume. Simultaneously, their triangular build restricts them to having a circular print bed, meaning they are ill-suited to printing large rectangular objects. Furthermore, their calibration process can be slightly more complex than a Cartesian model, potentially posing a challenge for beginners.
The Details about Cartesian 3D Printers
Understanding Their Traits
As the name suggests, Cartesian printers operate on a Cartesian coordinate system, moving along the X, Y, and Z-axes. Due to this, they typically boast large build volumes, which increases their adaptability for various uses. Their structure is typically box-like, open or closed, with a lot of the mechanical parts visibly moving as the print head is directed towards its location.
Benefits of Choosing Cartesian
One of the main benefits of Cartesian printers is their large build volume. Because of the more straightforward design, these types of printers often have the capacity to print larger objects without losing precision. In addition, Cartesian printers provide additional features such as the ability to use multiple print heads and multi-material printing.
Cartesian Printer Downsides
Despite these advantages, Cartesian printers are not without their own drawbacks. The primary one being speed. The heavier print heads in Cartesian models often have to move much longer distances than in Delta designs. This more substantial movement generally equates to slower print times.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which printer is best for beginners?
Although both printers have their advantages, Cartesian 3D printers, with simpler calibration and larger build volumes, are generally more suitable for newcomers to 3D printing.
Which printer delivers higher print quality?
Both types of printers can deliver high-quality prints. However, due to its lighter print head and lower vibrations, a Delta printer might have a small advantage in terms of producing intricate, high-resolution prints.
Final Thoughts
While we’ve explored the overall features, advantages, and drawbacks of both Delta and Cartesian 3D printers in this article, the ‘best’ choice ultimately boils down to your specific needs, usage expectations, and the types of projects you aim to undertake. Assessing these factors will help you make the right decision each time. And remember, while one printer might be ideal for a particular task, that doesn’t mean it won’t perform well in other areas, or that the other printer type couldn’t do just as well. In 3D printing, as with many things in life, versatility and adaptability often reign supreme.